Since 1960, interest into the nature and value of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) within organizations continues to grow. it becomes increasingly desirable to establish a tactical linkage between the strategic benefits of EDI and observed operational value.
Electronic Data Interchange or EDI, is the electronic exchange of business data using a standardized format. Simplistically put, the EDI process lets a company transfer data to another company electronically without using paper. EDI has continually shown significant business value by reducing costs increasing speed, accuracy and business productivity. The most significant EDI advantages often come at the tactical business stage.
According to the latest research study, Electronic Data Interchange continues to prove its worth as a leading electronic message data setup. The research also points out the yearly volume of total EDI transactions surpasses 20 billion per year and is still on the rise. With EDI, businesses can save millions of dollars annually due to new reimbursement rebates. From a financial viewpoint alone, there are remarkable benefits from applying EDI. However, saving cost is not the only benefit attached to EDI.
What is Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)?
EDI is the virtual exchange of business data or documents between trading partners through the electronic format. Document exchange is usually between buyer and supplier. The process comprises of transferring invoices, payments, purchase orders, shipping notices, and other needed documents electronically, thus eliminating any paper trails. EDI seeks to enhance virtual exchanges and improve operational efficiency with your trading associates. With EDI, any business can effectively communicate with another company globally without wasting time and estimating future actions.
EDI allows for better and more efficient collaboration with your suppliers. It also pushes costs out of the supply chain by removing wastefulness and manual involvement. EDI solutions are perfect for seamless integration into large and small networks of suppliers. No matter who you are trading with, a large or small number of SME suppliers located locally or internationally, EDI can assist with any business and technical necessities while providing support and resources to manage.
Whether your business requires an EDI Entry to exchange forecasts, invoices, orders, or other related business documents with your partners and suppliers, 100% integration can be achieved without much stress.
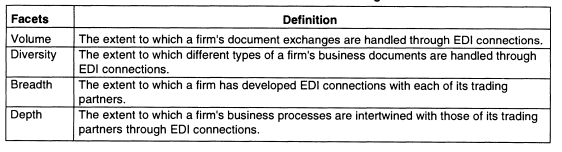
According to Massetti and Zmud (1996), there are four distinct facets of EDI: volume, diversity, breadth, and depth that, when aggregated, allow for a robust assessment of EDI usage. Brief definitions are presented in the below table.
11 Benefits of EDI
Applying EDI to your business setup can add extra value to your company’s process with automatic information processing, reduce clerical responsibilities, and remove data entry errors. The benefits of EDI for the end-to-end transactions use throughout the business cycle result in better use of time and resources.
This is a process that allows you to send information electronically rather than using paper. Reliable tools such as sodapdf filler can be a great way to streamline your communication.
Below are 11 known Benefits of EDI:
1. Better Speed:
EDI decreases the time it takes for an employee to make invoices and handle purchase orders manually. Timing is crucial when it comes to processing of an order. With EDI, businesses can speed up their cycles by 61%, creating an allowance for more automation process that significantly reduces, if not eliminate, time delays related to manual processes that require you to compare, enter, and file data. Records management is reorganized and made more effective with simultaneous data updates. Transferring documents electronically improves transaction speed and perceptibility while reducing the cost involved in manual approach. Stock levels are also kept regularly updated and visible.
2. Business Efficiency.
For the reason that human error is lessened, businesses can profit from improved levels of proficiency. Rather than focusing on everyday and tedious activities, staff can dedicate their attention to more significant value-adding tasks. EDI transfer guarantees immediate processing and eradicates time wasting related to manual entering, receiving, and sending orders. Improved quality of data provided by EDI lessens data entry errors, improves accounts activity times as procedures become efficient and can be made available for forecasting.
3. Collective Productivity.
The EDI technology permits more businesses to take on more operations with less human resources. Business teams can handle tasks with advanced additional worth. With EDI, the whole process is completed in a matter of seconds. This is due to the reason that automated process allows for instant completion of tasks like registering and balancing validation.
4. Cost Savings
This is among the most popular benefits of EDI. With EDI, the costs for processing business documents get at least 35% cut, but it can be much more remarkable in the case of electronic invoices, with 90% savings a possibility. Then again, this extreme economic saving is due to transactions automation and, also, the less involvement of paper usage. EDI reduces your operating outlay by removing the costs of document retrieval, filing, mailing, paper, postage, printing, recycling, reproduction, and storage. EDI significantly reduces administrative, maintenance, and resource costs.
5. Enhancing Financial Ratios.
With the Implementation of EDI, transferring and getting e-invoices takes place almost instantly. EDI also adds automatic authentication and checking procedures, which enable rapid dispensation at the endpoint, aiding in estimating cash necessities. In appreciation of this foresight, customers can take advantage of quick payment rebates and the dealer’s liquidness is enhanced.
6. Environment-Friendly Services.
The movement from paper-based services to electronic transactions available on EDI decreases CO2 discharges. Thus, the use of EDI encourages corporate social accountability and help the organization achieve sustainable supply chain management.
7. Information Availability on Process Status.
Replacing paper with e-documents makes it easy to maintain and track data. EDI safeguards traceability and transaction integrability like changes to purchase orders, invoices, pending payment status, receipt acknowledgement, and other similar events. Additionally, sending data through private networks make available lasting control over message status about processing, reading, and receipt, etc.
8. Improved Accuracy
Apart from inadequacy, the manual approach is also highly susceptible to error, usually resulting from entering and re-keying errors, indecipherable handwriting, and improper document management. EDI considerably improves your business data quality and removes the problem of re-working orders by bringing at least a 30% to 40% drop in transaction errors. The use of ethics acknowledged by both parties (receiver and sender) guarantees correct interpretation of data, irrespective of activity sectors or nationalities.
9. Operations Automation.
The benefits of EDI tool considerably lighten the management burden. Several tasks, like enveloping, franking or registering, printing out business documents, would fade entirely. EDI’s adaptableness modernizes the communication flow and improves typically business relations with other trade partners.
10. Refining Service to Partners and End Users.
Implementation of EDI implies the application of optimal workflows and response time. Implementing EDI benefits the end user most of all, as manufacturing plans and distributions become much more accurate. EDI also enlarges your customer base and manages trade partner relationships due to its quicker goods and services distribution.
11. Security
EDI boosts the level of protection for any transactions by strongly allocation data across a more extensive variation of communicating protocols and safety standards, hence, reducing supply chain risks. Your trading partners would profit from the seamless movement of data and accessibility to the technology creates prospects for newer business breaks.
5 Limitations of EDI
While countless businesses enjoy the benefits of EDI, some companies are still cautious to try it out due to the following limitations of EDI.
1. Cost of Implementation.
It is true that EDI provides massive cost savings benefits but for small businesses re-designing and implementing software applications to fit in EDI into current applications can be quite costly. Such limitations of EDI must be considered if you plan on implementing such system.
2. Electronic System Safety
EDI also necessitates substantial investment in computer networks and security systems for maximum security. Any EDI system installed would require protection from hacking, malware, viruses, and other cybersecurity threats.
3. Preliminary Setup Consumes Time
Not only is the implementation of EDI system expensive to install, but it also consumes a considerable amount of time to set up the essential parts. Thus, such limitations of EDI can hinder fast-tracking of services if urgently required.
4. Several Standards to Maintain.
Numerous businesses looking to implement EDI also consider the several standards involved. These limitations of EDI do not allow small businesses to exchange data with larger establishments that make use of latest edition of a document standard. Some known measures include ANSI ASC X12, GS1 EDI, HL7, TRADACOMS, and UN/EDIFACT.
5. Suitable Backup System
EDI implementation also requires regular maintenance as the business functionality is highly dependent. Some robust data backup system is needed in case of a system crash or for statistical purposes. Such limitations of EDI can cost a substantial amount to implement.
Measures of Implementing EDI Success Factors
The fruitful implementation of EDI is based on conditions that determine the EDI-based systems to be installed and operated in a way well thought-out as successful. Additionally, to simplify expressive evaluations to match your business needs, below are five measures to note in Implementing EDI Success Factors, based on other prevailing EDI execution:
- The Degree of Acceptance of EDI Within Your Business.
- The Degree to Which Objectives Is Met by The Systems.
- Fiscal Payback.
- Level of Integration with Current Systems
- Present Level of EDI Usage
1. The degree of Acceptance of EDI Within Your Business.
EDI execution encompasses more than just one business setup. This implies that every partner or possible trade exchange has to considered differently from your general EDI implementations. You are required to plan along and determine what future services can be added to the system. A list of non-technological and technological factors can be identified by top personnel within your business as to what is central to a successful EDI implementation.
2. The degree to Which Objectives are met by The Systems.
Every organization needs to decide at the preliminary stage the level of EDI implementation success is required to be called a victory. Your average organizational experience on EDI-based systems also matters as it usually is considered as key to its operation. It is also believed that all EDI application involves more than technological matters.
3. Fiscal Payback.
EDI is not just about achieving cost savings measures. To enjoy the most benefits of EDI, the implementation is required to focus primarily on solving business-related problems. If this measure can be achieved, then your business can avail itself to excellent benefits of EDI like more effective processes.
4. Level of Integration with Current Systems
The critical area of transformation acknowledged by most businesses is the additional complexity brought in by EDI. It extends beyond any organizational boundary and value-added links. This measure is a necessary change that affects functions and processes within your business and its transverse border. The level of integration with current systems asks questions like what additional concerns are created? And how willing are you ready to go in changing your compatibility, planning, and trust process?
5. Present Level of EDI Usage
During the early stages of execution, the nontechnological and technological factors are equally important to the level of the skillset of your workforce. Nevertheless, once the EDI platform is in place, the nontechnological factors assume more importance about other technological factors. These factors are known to cause more problems, thus forming a critical measure that needs tackling.
CONCLUSION
Today, most trades accepting to roll out EDI systems do so convince of the attached benefits of EDI will bring to their overall organizational structure. Everyone can acknowledge the benefits of EDI as a communications technology. However, some still fail to observe and make good use of the possible advantages the integration of electronic data transmission and a paperless system can offer their business. EDI standards would continually remain a leading protocol in the B2B space.
For smaller organizations, it is all about efficiency and speed. They are changing all labour-intensive paper processes and slow, monotonous cycle with a faster, more precise electronic system that speeds up everything. It implies that impresarios can redistribute precious resources into more valuable ventures. On the other hand, Larger organizations with EDI-enabled networks can benefit from consistent, integrated, and streamlined business procedures. The real-time data available about other trade partners aid managerial decisions in building better strategic connections, encouraging buying and supplying to work together seamlessly.
Free from any directorial problem, participating businesses can emphasize what they perform best, creating long-term associations with clientele, evolving new products and services and initiating new marketplaces. Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) is the absolute game-changer for last four decades!!
Reference:
Massetti, B. and Zmud. R. W. (1996) “Measuring the Extent of EDI Usage in Complex Organizations: Strategies and Illustrative Examples”, MIS Quarterly, Vol. 20, No. 3, pp. 331-345
Recommended Reading:
E*D*I – Electronic Data Interchange: An introduction
Implementation of Electronic Data Interchange: Electronic Data Interchange
EDI Concept (Electronic Data Interchange): Benefits of exchanging electronic documents and strategies for implementation.


Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the positives of EDI?
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) offers several advantages for businesses. Firstly, it enhances efficiency by automating the exchange of business documents, reducing the need for manual data entry and minimizing errors. Secondly, EDI promotes faster and more accurate transactions, leading to improved overall productivity and customer satisfaction. Additionally, it facilitates better communication and collaboration between trading partners, streamlining supply chain processes and contributing to cost savings over time.
What are the features of EDI?
Standardization: Adheres to established data interchange standards.
Automation: Enables automated document processing and exchange.
Security: Utilizes encryption and authentication for secure data transmission.
Efficiency: Reduces manual data entry, minimizing errors and processing time.
Compatibility: Integrates with existing business systems and software.
Reliability: Ensures accurate and timely data transfer between trading partners.
Audit Trail: Provides a record of document exchanges for tracking and compliance.
Cost Savings: Streamlines processes, reducing paper usage and operational costs.
Scalability: Scales to accommodate growing business needs and transaction volumes.
Global Reach: Facilitates international transactions and collaborations.
What are the three components of EDI?
Translation Software: Converts business documents into a standardized EDI format for transmission and translates incoming EDI documents back into a format that can be understood by the recipient’s internal systems.
Communication Software: Facilitates the transmission of EDI documents between trading partners. This can include Value-Added Networks (VANs), which act as intermediaries for secure data exchange.
Application Integration: Involves integrating EDI data into the internal systems of the businesses involved. This ensures seamless communication between EDI and the organization’s enterprise resource planning (ERP) or other business software systems.
What is EDI syntax?
EDI syntax refers to the set of rules and conventions that define the structure and format of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) documents. It establishes a standardized language for representing business data in a machine-readable format, allowing for consistent and efficient communication between different computer systems. Common EDI syntax formats include ANSI X12, EDIFACT, and XML, each specifying how data elements, segments, and documents should be organized for accurate and reliable electronic exchange of business information.
About the Author- Dr Muddassir Ahmed
Dr MuddassirAhmed is the Founder & CEO of SCMDOJO. He is a global speaker, vlogger and supply chain industry expert with 17 years of experience in the Manufacturing Industry in the UK, Europe, the Middle East and South East Asia in various Supply Chain leadership roles. Dr. Muddassir has received a PhD in Management Science from Lancaster University Management School. Muddassir is a Six Sigma black belt and founded the leading supply chain platform SCMDOJO to enable supply chain professionals and teams to thrive by providing best-in-class knowledge content, tools and access to experts.
You can follow him on LinkedIn, Facebook, Twitter or Instagram